Freezers & Chillers
In a typical frozen foods manufacturing facility, and many ambient baked goods sites, there are various types of industrial refrigerators and chillers employed to maintain consistent quality, texture, and temperature of products.
Spiral freezers and chillers are one means of refrigeration that are popular with food processors, given their compact spiral belt and their ability to freeze or chill large numbers of products with longer dwell times.
Spiral blast-freezing of food products is the most energy intensive process in a typical frozen foods manufacturing facility, with air temperatures regularly in the range of +5C to -40C depending on the type of product to be frozen or chilled.
Unlike tunnel freezers, which require a long, linear wiremesh belt to convey products through a sub-zero blastfreezing room, spiral freezers use self-stacking, multitiered belts to maintain product quality and minimize the refrigeration space required in the plant. Most modern spiral freezers offer a high level of customizability and are generally fairly easy to install on the plant floor.
Potential Savings using RS Industria.
£0
Potential Savings in Energy Costs
£0
Reduction in Wastage
Overview
Freezers and chillers are essential to protect food quality and safety. Serving a vital role in extending shelf life, they help to reduce waste and increase profits – all while preserving freshness and flavour, as well as ensuring that products are available year-round to meet consumer demand.
RS Industria can help you to guarantee quality by unlocking the hidden information that has been stored in your freezers and chillers – releasing new-found insights to boost operational performance, reliability, and sustainability.
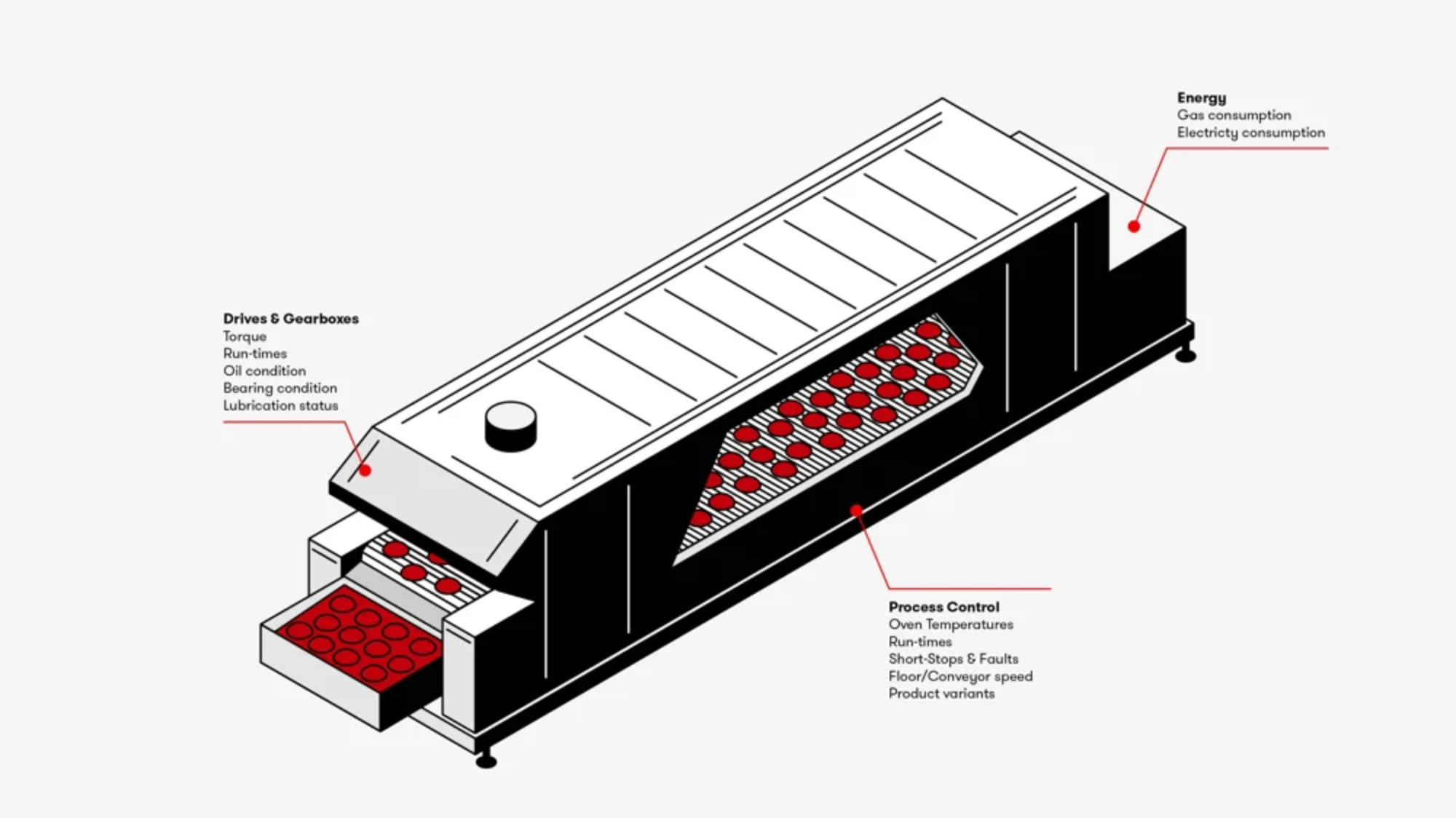
Energy Consumption
The Challenges
Spiral freezers are expensive to operate as they typically run at low temperatures. Often, the suction pressure of the plant’s refrigeration system (which defines the energy used in the refrigeration plant) is determined by the temperature needs of the spiral freezer. Most spiral freezer systems are not optimized as many of the key parameters such as airflow and the entering & leaving temperatures are not controlled.
Many manufacturing facilities employ multiple spiral freezers. However, by managing the entire freezing process with the right advanced monitoring and controls systems in place, plant operators can achieve energy savings of between 30% to 50% or more on an annual basis.
Our Solution
The main energy use in the chiller is the cooling process, typically supplied by a centralised ammonia refrigeration compressor and distributed throughout the site; either directly as ammonia, or indirectly through a glycol system. Energy transfer from the cooling fluid to the chiller can be measured by monitoring the flow rate and temperature of the cooling fluid.
Energy consumption for the belt drive motor can be easily measured either from the inverter drive or through using CT clamps on the power line.
Book an Energy Consultation to find out how much you could save!
Your Benefits
Spiral freezers are large consumers of cooling from the refrigeration compressors. A 500kg/hour freezer, operating at -20C typically consumes circa 250kW of cooling.
Assuming your fridge has a CoP of 3, this represents about 80kW of electricity, or around £100,000/annum cost (at June 2022 prices). Improving heat transfer by 10% will save around £10,000 per annum.
£10,000 Energy Annual Saving
Operations
The Challenges
Spiral Freezers and Chillers generally have few significant operational challenges
Our Solution
Where the chiller is controlled by a local PLC, this data can easily be collected to enrich the energy and maintenance data, providing vital operational context for each of the operating modes (such as production or defrost).
Your Benefits
These items of equipment are such that, from an operational perspective, there is limited opportunity to improve.
Maintenance
The Challenges
The chiller is a critical asset on any production line, and the line cannot run without the chiller. Lines are typically used continuously and have minimal maintenance windows due to production requirements, so active protection of this critical asset is essential, as chillers often have little or no installed condition monitoring and rely on Planned Preventative Maintenances to find potential failures.
Our Solution
Typical failure modes on spiral chillers are:
- Chain snagging due to poor synchronisation of the drive motors, leading to the drive chains snapping.
- Water contamination of the gearbox oil due to condensation from the heat / chill cycle, leading to early failure of the gearbox.
- Wrong choice of gearbox lubricant as people often use an ambient oil, which then turns to grease when at lower operating temperatures.
- Rarer, but catastrophic if it happens, is failure of the main bottom bearing or the shaft. To provide early warning of these potential failures, enabling maintenance teams to take prior action to avoid or mitigate failure, we would recommend:
- Collecting all available drive and current consumption data from the motors as this often shows very early indication of the mechanical degradation, as well as potential rotor / stator failure in the motor
- Continuous monitoring of the gearbox oil with a suitable sensor to monitor the water content of the lubricant, its temperature, and any ferrous contamination from gear box wear.
- Vibration monitoring on the motor/gearbox
- Ultrasound monitoring of the bottom bearing/bush as the slow rotational speed makes vibration monitoring ineffective.
Your Benefits
A typical failure could take 24 to 48 hours to fix and lead to a shutdown of the line. At an operating value of around £1,000 per hour, together with the scrapping of all the product currently on the line, the consequence of failure could easily be in excess of £50,000.
£50,000 Maintenance Annual Saving
Increase Safety
Reduce Waste
Unleash Your Factory's Potential
Find out how we can help lower energy usage, enhance reliability and improve operational performance: in a way that is simple, fast and affordable.
Book a Demo

