DAF - Dissolved Air Flotation
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank basin.
The released air forms tiny bubbles which adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where this layer of sludge is removed by a skimming device. Flocculants and coagulants are often added to improve the performance of the unit.
Dissolved Air Floatation performance depends on the air to solids ratio, and this will vary with different types of suspension as the floatation process is dependent on the surface area of the materials.
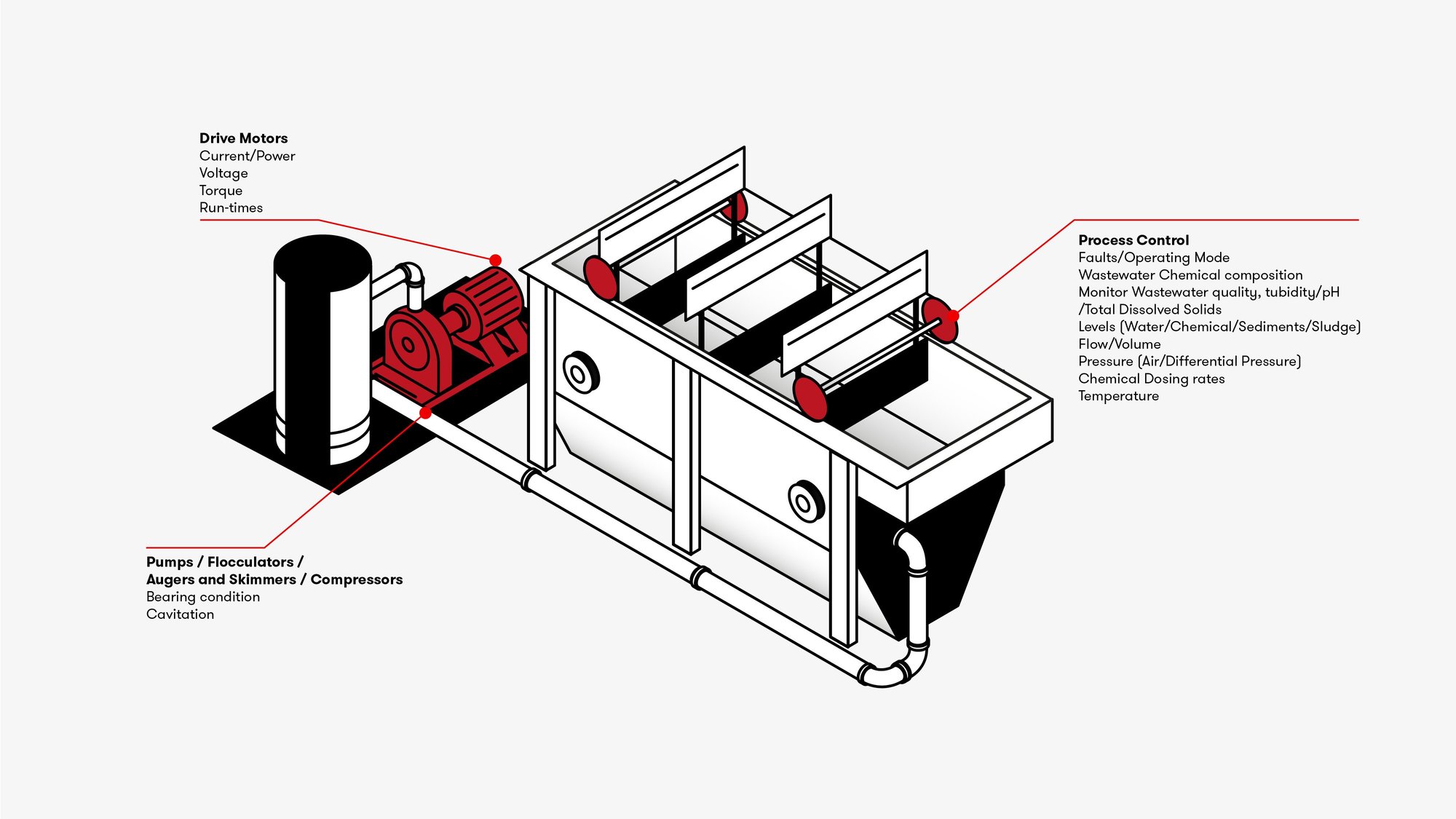
Overview
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a water treatment process that separates suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants from water, before it’s discharged or further treated.
Fine bubbles of air are introduced to the water, which attach to suspended particles and cause them to float to the surface. The floating particles form a thick layer of sludge or froth, which then can be skimmed off and removed.
DAF systems typically have shorter hydraulic retention times when compared to other treatment processes, such as sedimentation basins; This results in faster treatment and increased throughput, allowing for higher treatment capacities.
With RS Industria, you’ll have the means to leverage the unused data stored in your DAF systems, giving you access to brand-new insights – leading to boosted operational efficiency, improved reliability, and even energy-saving action points to shrink your carbon footprint and cut costs.
Energy Consumption
The Challenges
Pumps, compressors and augers are heavy energy users, but the energy consumption often goes unnoticed as most DAF units operate unmonitored. Most pumps and compressors are stop/start as required, meaning energy consumption is hard to capture
Our Solution
Energy data can often be collected direct from the variable/ fixed speed drives, when used. If no electrical consumption data is available, then energy meters or current transformers can be easily installed, which can pass data directly to RS Industria.
Book an Energy Consultation to find out how much you could save!
Your Benefits
The site can now quantify the energy costs of pumps, compressors, flocculators and augers, including highlighting wasted energy from overoperation (running without purpose). The data also enables pump and system efficiency to be monitored.
Operations
The Challenges
pH inconsistencies can result in potential damage to equipment, non-compliance waste regulations and the inhibition of some coagulants used in wastewater treatment, as they are only effective within a neutral pH range. Substantial chemical usage can be required to rectify any water quality issues, if left unobserved.
Typically, the volume and air setpoints are set manually to achieve the desired air to solids ratio in a DAF system. The dosing rate of flocculant or coagulant is set to efficiently treat a certain concentration of contaminants. Most DAF units will not automatically adjust the settings for fluctuations in wastewater quality.
Our Solution
Water quality process data such as pH, Turbidity, Total Suspended solids (TSS), Dissolved Oxygen (DO) and Temperature levels, can be monitored directly from IoT instrumentation on the DAF system or directly from a PLC or control system. Where no input is currently recorded, hardwired signals can be extracted through IO gateways to mirror existing control signals. This will provide valuable accurate operational recording as well as aid in problem solving.
Various flow rate data can also be extracted, and total volumes can be calculated, including chemical dosing rates.
Your Benefits
Enable increased efficiency with better management and reduction of chemical usage for coagulants and other agents used to meet effluent quality compliance levels.
Data trending of water quality can inform the site when to dose additional chemicals or dilute tanks with less contaminated influent.
Remote monitoring of assets improves staff productivity as well as highlighting problems early.
Maintenance
The Challenges
Unplanned bearing failures of pumps, compressors and augers can occur if static for too long (Standby) or due to duty pump mechanical stress transfer, along with other mechanical issues such as looseness and misalignment of the asset. Pipework restrictions often go unnoticed until blockage occurs. A loss of a critical component could result in a plant and whole site stoppage due to the inability to process waste.
Chemical corrosion and degradation of equipment and components are also common problems that often go unmonitored.
Our Solution
Through tracking current and torque, changes in the electrical load can be used to indicate changes in the system. Using the additional process parameters, we can build a picture of how the asset performs from a reliability standpoint.
Additional protection of the motor and pump bearings can be added using a vibration sensor, thus monitoring mechanical stresses such as looseness, misalignment, impeller wear and cavitation.
Pressure analysis can indicate blockages or valve malfunctions.
Your Benefits
Monitoring reduces the risk of unplanned failure, so removes the potential for secondary damage as well as the cost of replacement components. Better data enables the site to move from reactive maintenance to planned maintenance, so reducing downtime of the mechanical equipment. If vibration data is collected, the site can determine the lubrication status of assets.
Monitoring also enables chemical compositions to be controlled within a low-corrosive range, increasing longevity of equipment within the DAF System.
Reduce Emissions
Avoid Breakdowns
Improve Operational Performance Now
Find out how we can help lower energy usage, enhance reliability and improve operational performance: in a way that is simple, fast and affordable.
Book A Demo

