Cooling Towers & Evaporative Condensers
Cooling towers and evaporative condensers are used to remove excess heat from a cooling system when the heat cannot be utilised for other purposes, with the excess heat removed by evaporating water.
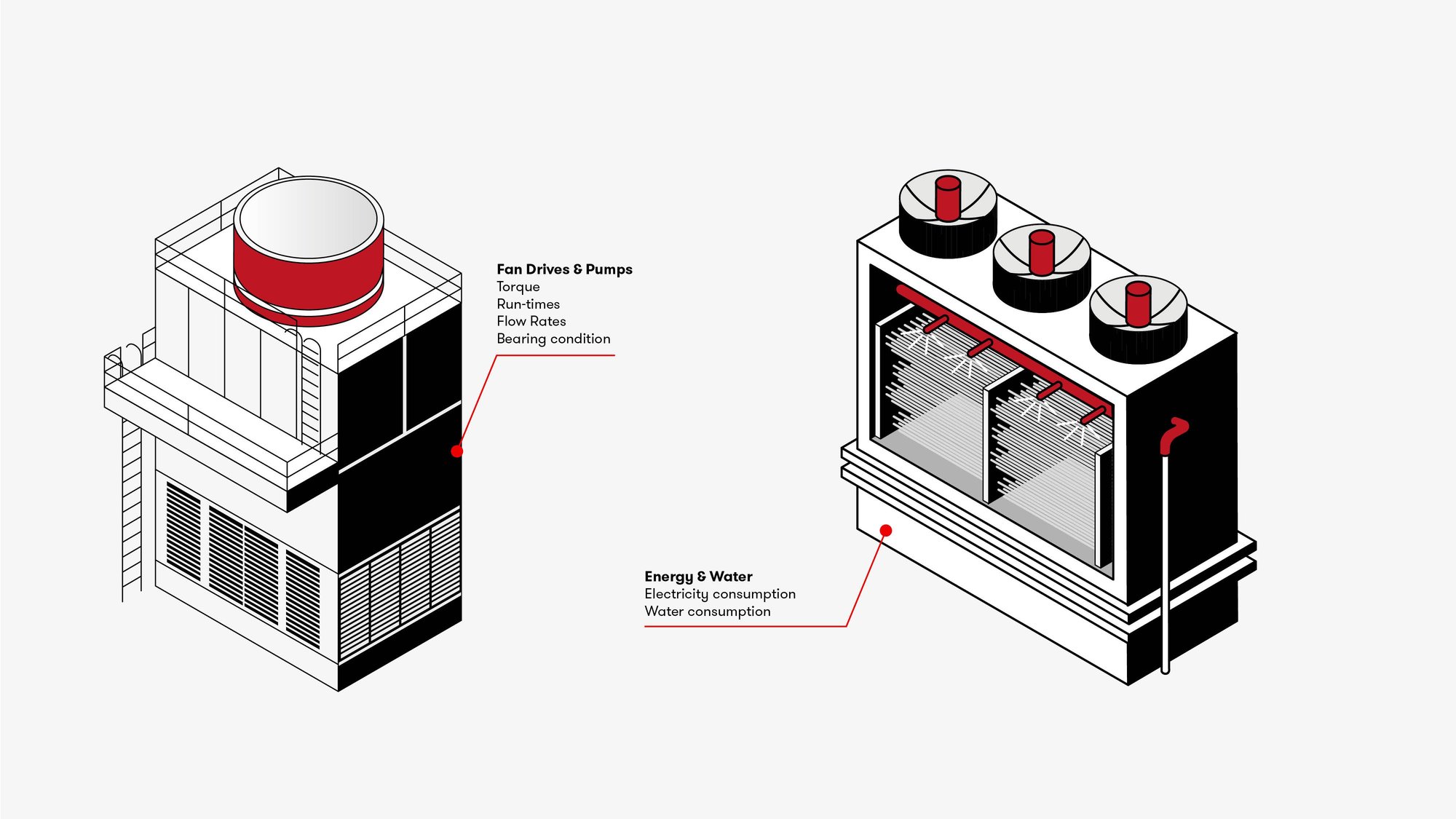
Often “out of sight, out of mind” in remote areas of the site or on the roof, they are critical process assets where failures can have significant impact on energy consumption, site operations or control of L8. Whilst relatively simple, the fans and motors operate in a wet environment exposed to the weather, and traditional condition monitoring techniques are unsuitable.
Overview
Cooling towers and evaporative condensers are used by factories to remove excess heat from cooling systems.
The surplus heat is removed by evaporating water in situations where the heat cannot be utilised for other purposes. Assets such as cooling towers and evaporative condensers are often out of sight in remote areas or on rooftops.
RS Industria offers digital conditioning monitoring to avoid neglecting such critical assets that are not are not always front of mind. Our simple, fast and affordable data-led insight maximises energy efficiency and prevents unforeseen downtime.
Energy Consumption
The Challenges
The biggest impact that performance degradation of a cooling tower or evaporative condenser has is on energy consumption, as a reduction in the efficiency of these systems will directly impact the efficiency of the system they are cooling, typically air or refrigeration compressors.
Our Solution
Continuous monitoring of the inlet and outlet temperatures, wet bulb temperature and make-up water consumption will provide early warning of any drop in efficiency. Temperature probes can be fitted to measure the hot water, cold water and wet bulb temperatures. Current monitoring can be fitted to measure energy consumption in the pumps and fans. Any reduction in the efficiency will indicate fouling of the tower pack, requiring cleaning.
Book an Energy Consultation to find out how much you could save!
Your Benefits
Degradation in the heat transfer efficiency of the cooling tower will directly impact energy consumption of the heat source. Due to the wide range of potential loads on a cooling tower, you cannot quote a typical saving.
Operations
The Challenges
The major operational risk is around controlling the growth of bacteria related to Legionnaires Disease. Conformance to the control procedures specified in the HSE ACoP L8 aim to inhibit the growth of this potentially dangerous bacterium, and are a legal requirement, strictly enforced by the HSE. Control is usually managed through water temperature control and the addition of biocide to the tank. Whilst biocide dosing systems are automatically controlled to ensure a minimum level of biocide, overdosing of chemicals can often be missed, increasing the cost of operating these assets. In addition, increased water consumption can indicate damage to the pack and the drift eliminators.
Our Solution
Extracting data from the chemical dosing system allows you to track chemical usage, indicating where overdosing may be occurring.
Your Benefits
Monitoring chemical use can identify overdosing, reducing the cost of biocides.
Maintenance
The Challenges
The nature of the wet, exposed environment that the fans and pumps in a cooling tower operate in can lead to both mechanical and electrical faults on the motors, whilst the remote location of the assets makes them harder to monitor through traditional timebased preventative methods.
Our Solution
The nature of the wet, exposed environment that the fans and pumps operate in means that techniques such as vibration analysis are not usually suitable for this type of asset. Using current consumption as a leading indicator of failure is a cost-effective method of condition-monitoring a cooling tower.
This can be achieved through either collecting data direct from inverters if fitted, or more typically, CT clamps on the supply. The same current monitoring used to monitor efficiency and energy consumption can also be used to provide early warning of potential electrical or mechanical failure of the rotating assets.
Your Benefits
Due to the wide variation of cooling tower and evaporative condenser types and deployments, indicative estimates of maintenance cost savings are difficult to create. Speak to our consultants for an indication based on your specific installation and operation.
Reduce Emissions
Avoid Breakdowns
Improve Asset Reliability
Find out how we can help lower energy usage, enhance reliability and improve operational performance: in a way that is simple, fast and affordable.
Contact Our Experts Today

